

We all have come across the term vapor pressure during our Science lessons. However, being able to recall or understand the concept efficiently might be a Herculean task for many.
To go through the basics again and to make things easier, find out below what vapor pressure is, its equation, formula for vapor pressure, and the factors affecting vapor pressure
When the process of evaporation is carried out in a closed space, the molecules are still in a state of motion. However, the molecules tend to lose their energy after some time and revert to their liquid state, which is known as condensation.
It is only after a certain point of time that equilibrium is established between the process of evaporation and condensation and molecules exert pressure on the surface of the liquid. This process is known as vapor pressure.
In simple terms, the vapor pressure is the term given to the force exerted by the vapors in equilibrium with liquid or solid substance while enclosed within a container.

(Image Courtesy: Youtube)
The vapor pressure formula is best demonstrated using Raoult's law by explaining how the vapor pressure can be altered by adding a non-volatile solute. According to this formula, with the addition of a non-volatile solute, the vapor pressure can be efficiently lowered.
The formula involves three elements, namely, P Solution, X Solvent, and P° Solvent. To elaborate, P solution is the vapor pressure of the solution, X solvent is the mole fraction of the solution, and P° Solvent is the vapor pressure of the pure solvent at standard conditions.
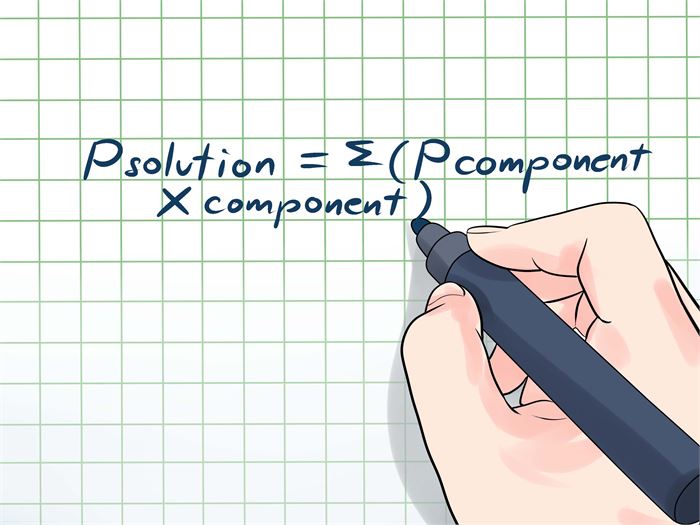
(Image Courtesy: Wiki How)
#1. Temperature
Temperature has the most significant impact on the vapor pressure as with higher temperature, the energy of molecules rises and there is an increase in their ability to escape. A lower temperature, on the other hand, makes it difficult for the molecules to escape from the liquid.

(Image Courtesy: BC Open Textbooks)
#2. Molecule Type
The intermolecular force and the vapor pressure are inversely related to each other. When the intermolecular force between the molecules is strong, the vapor pressure will be low. However, if the intermolecular force is weak, the vapor pressure is likely to be higher.
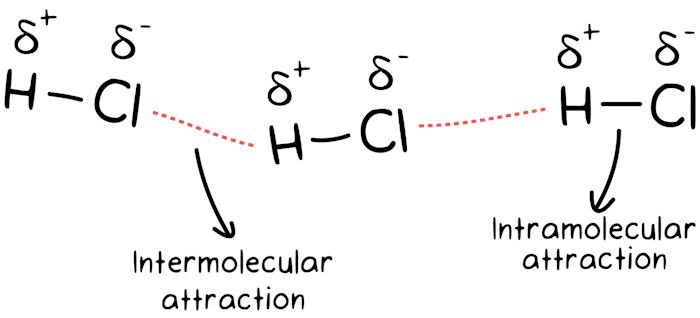
(Image Courtesy: Khan Academy)
#3. Surface Area
As against the other factors, the surface area of the solid or liquid will have no impact on the vapor pressure. In other words, it will hardly matter whether you use a larger surface area or a smaller surface area, the vapor pressure will still be the same with constant molecule type and temperature.
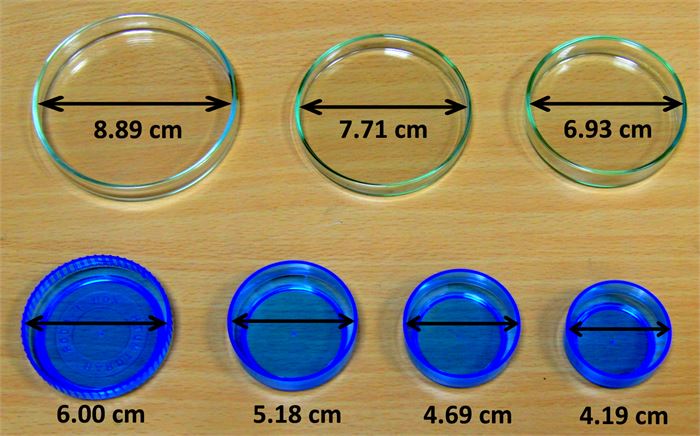
(Image Courtesy: Fyzikalnipokusy)
If you know something more about the vapor pressure, we would love to hear from you. Kindly use the comment box to share your thoughts and opinions with us.
(Featured Image Courtesy: SlideShare)