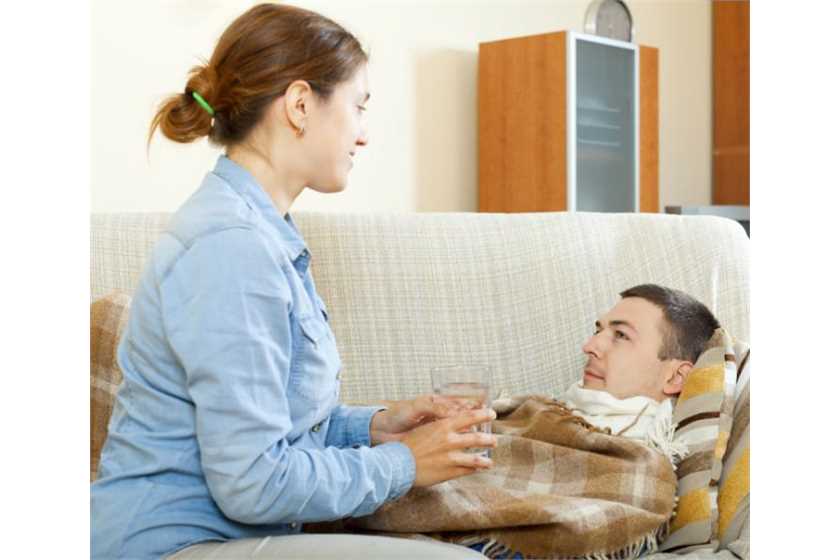


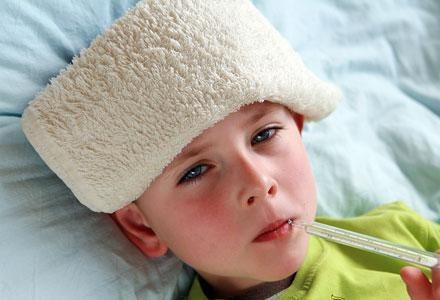
Fever is characterized by a temperature higher than the normal body temperature ie. 98.6F caused by many possible reasons and associated with various clinical symptoms. Because fever is the body’s natural defense mechanism, it is a common occurrence with any cause of infection or illness. Thus, until the body temperature rises above 100F, it does not necessarily require an urgent medication in case of adults, unless the other symptoms attribute to a critical condition for the body. The seriousness of a similar fever in case of babies or infants may be much more and has to be addressed immediately with proper clinical advice.
The causes of fever could be many, of which viral or bacterial infections, increased exposure to extreme heat or cold, clinical conditions such as arthritis or cancer, certain antibiotics or drugs and immunizations, are common. Sometimes, exhaustive exercising or menstruation could also lead to fever. A fever for which a cause cannot be explained is a greater reason for worry, particularly for children. Inability to respond to the mother, listlessness, irritability, frequent vomiting and high body temperature for more than three days, are among a few symptoms in fever among children which should not go unaddressed. However, the following symptoms are common and generally associated with fever:
• A headache and sore throat
• Skin rash
• Body pain and muscle weakness
• Mental confusion and listlessness
In critical situations, vomiting, tightness in the chest or suffocation, stomach pain, and neurological deficits may be attributed to high fever.
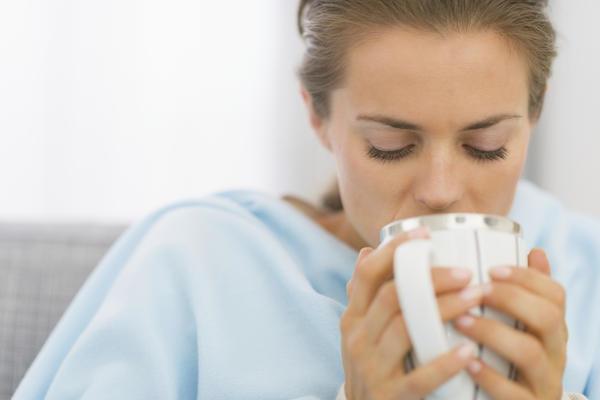

The most common strategy for treating fever in children and adults who are not undergoing chemotherapy or do not have immunological disorders includes primarily the intake of fluids in large volumes and adequate body rest. To relieve pain or irritability accompanying a high body temperature, doctors have to be consulted before the intake of any pain reliever or medication for fever, and the dosage of medicine has to be taken care of when being administered in both children and adults.

The common cold is a respiratory illness caused by viral infections, especially rhinoviruses. The mode of entry of these viruses into the body is through the nose, eyes, and mouth through physical contact or exposure to infected objects of the patient. Droplets of a cough, due to sneezing or coughing in the environment, when transmitted through air increases the susceptibility of an individual to developing a cold. Generally, considered milder than the flu, some of the factors further worsening the symptoms of a common cold include a weak defense system and smoking. In general, it is never so serious that a doctor needs to be consulted to seek a treatment for common cold and no specific medication can be prescribed for its cure.
The common symptoms of common cold include:
• Running nose and sore throat
• Sneezing and chest congestion
• Fever, body pain, and headaches
In certain extreme cases, when common cold accompanies other symptoms such as ear infections or otitis, asthma attacks, infection of sinuses (sinusitis), bronchitis or pneumonia, it needs medical attention. Wheezing, breathlessness, extreme pain, physical weakness, and loss of appetite, are some of the potential risks demanding emergency clinical advice, particularly when affecting children and infants.

Though there is no specific medication targeting viral infections, antibiotics against cold are prescribed and can be effective only when caused by bacterial infections. To ease out pain, headache or other symptoms accompanying cold, mild pain relievers are prescribed by doctors. Being cautious about the dosage and ensuring prevention of symptoms from manifesting in the body must be compulsorily addressed while strategizing its treatment. Only pain medications suitable for children should be administered in proper doses to infants.

Cough syrups are generally not prescribed for children under the age of 4 years. Even if advised, no two medicines with the same composition or efficacy in relieving symptoms are recommended for children, owing to its overdose. Nasal sprays can be used by adults to combat congestion, however, is not generally desirable for children aged below six years. Incorporating vitamin and zinc supplements in the diet are also suggested approaches towards seeking a cure to common cold, ideally requiring almost ten days for the symptoms to be eliminated completely.

Relative to the common cold, the flu is a contagious disease affecting the respiratory system and is generally considered more severe. Also caused by viruses, the risks or complications arising from flu are attributed to the extent that it could cause serious health disorders and ultimately result in death.
The manifestation of flu symptoms are sudden and generally include:
• Fever and fatigue
• Body pain and muscle fatigue
• Running nose
• A sore throat and cough
Some of the chronic medical conditions arising from flu are common among the youth, adults above 65 years of age, pregnant women, and those who are terminally ill with a persisting clinical condition. In an extremely demanding situation, lung infection and pneumonia arises could result from chronic flu episodes. The risks of developing inflammation of the heart (myocarditis), brain (encephalitis), muscle tissues (myositis) and the failure of kidneys, sepsis or asthma can further accentuate the expected symptoms of flu in chronic situations.

As a natural remedy for relieving symptoms of flu, it is desirable to consume plenty of fluids, to take rest and keep warm. Anti-inflammatory medicines prescribed for controlling fever and body ache are effective, but medicines like aspirin should not be recommended for children aged below 16 years. Antibiotics are not generally available for the cure of antiviral infections, however, may be effective in the case of a bacterial infestation resulting in flu. Most of these medicines find an effect in reducing the symptoms and the period of illness.
Fever, cold, and, flu are illnesses with overlapping symptoms and causes. However, the intensity of its severity is determined by the age group it affects and thus, the protocol for treatment and cure has to be carefully decided by its clinical manifestation.
