

Programmers have faced a serious issue of how to stop doing a particular type of coding for two times or more. In the programming world, we find similar situations time and again. If we do not have some mechanism to reuse the code effectively and get it quickly adapted to various similar situations, we cannot expect faster programme development. And it could be crucial. In the industry, time is being sold actually and more time means more expense that will not appeal the clients.
So more time in a programme development means high chances of losing the project.

Design Pattern
This is where the design patterns come forth. A design pattern is a common solution to a particular type of design problem.Years of experience of veteran programmers has given birth to several design patterns that are effectively used while programming for a particular type of problem. And there are many types of design patterns.
MVC or model-view-controller design pattern is one of them. A model-view-controller design pattern divides the solution into three parts:
MVC in PHP
In PHP, there are many MVC frameworks in the market. CodeIgniter, Laravel, CakePHP,Symfony,Zend Framework, Yii, Aura are some of them. The credit of CodeIgniter is that it is a lightweight framework and it is still very rich in resources. And it is free, too.
Active Records
The active record pattern is an architectural pattern used in a software that stores in-memory object data in relational databases. If an object conforms to this pattern, its interface would include functions like Insert, update, and delete, in addition to the properties that correspond more or less directly to the columns in the underlying database table.
So basically the active record pattern is an approach to access data in a database. A database table or view is contained in a class. This pattern is generally used by the object persistence tools and in object-relational mapping (ORM).
Object-relational mapping (ORM, O/RM, and O/R mapping tool)
This is a programming technique for transforming data between the systems which are incompatible. This forms a "virtual object database" which can be used from within the programming language.
Active Record in CodeIgniter
CodeIgniter uses a modified version of the Active Record Database Pattern. It permits information to be retrieved, inserted and updated in the database with minimal scripting.We can create database independent applications in CodeIgniter. There are several database adapters that actually generate the query syntax.
Libraries: CodeIgniter has many libraries of classes useful in many programming situations.
Helpers: These are the collection of functions useful in many programming situations.CodeIgniter has helpers to assist us.
Customization: CodeIgniter is rich in resources and the best thing is that we can customize them as per our need.
User Guide :The user guide is available at the URL http://localhost/ci/user_guide/ The link to the user guide is also given on the index page.
Installation
We can download CodeIgniter at https://www.codeigniter.com/. To install it in our computer we simply need to put the CodeIgniter folder in the htdocs folder. And it is done.
Running
http://localhost/ci : Suppose the name of the CodeIgniter folder is ci. Then put this address in the address bar and enter! We get the following page:
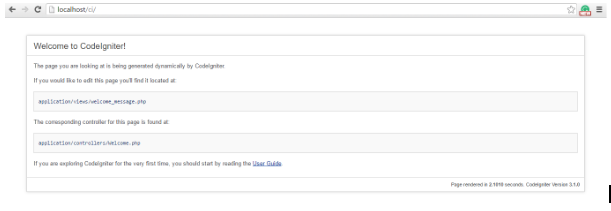
Directory Structure
CodeIgniter has the following folders:
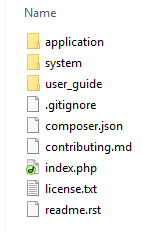
System Folder
It is the collection of core functionalities.
User Guide Folder
It contains the user guide.
Index.php
http://localhost/ci/index.php : This is an important file. If we have to use any part of an application, that is done through index.php. When we call a method, we put the following in the address bar:
base url/index.php/controller/method
i.e.: http://localhost/ci/index.php/controller/method
If we do not give the name of the controller, the default controller is run. If we do not give the name of the method, the index method is run.
Here, the controller and the method are being passed to index.php as parameters.
Note: In the URL, we can remove index.php and use: http://localhost/ci/controller/method, but for that, we need to configure .htaccess file.
The Application folder
It contains the folders namely models, views, controllers,config and many more.
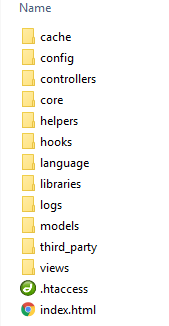
Models: Database and other forms of data
View: Front End (say HTML, Javascript etc.)
Controller: It controls and coordinates Models and Views.
Config: It has the following sub-folders:
autoload.php : application/config/autoload.php
This file specifies which systems should be loaded by default.
config.php : application/config/config.php
It sets the base url:
$config['base_url'] = '';
$config['index_page'] = 'index.php';
etc.
database.php : application/config/database.php
Database configuration is done here.
routes.php : application/config/routes.php
A specific controller is hit when we put the base url ( http://localhost/ci/ )in the address bar. That default controller is set in this file:
$route['default_controller'] = 'welcome';
Also the page not found controller is set there:
$route['404_override'] = '';
Controller
It is basically a class. We create a .php file in application/controllers with the same name as that of the controller we are to create. And in this file, we write the class with the same name.But the first character of the controller name should be capital. The class should extend CI_Controller.
Note: If we do not extend the class, it would run, but we could not use the inbuilt functionalities of CodeIgniter.
class Welcome extends CI_Controller
{
public function index()
{
$this->load->view('welcome_message');
}
}
This controller calls the view: welcome_message.php
In this file, at the top, there should be:
defined('BASEPATH') OR exit('No direct script access allowed');
As we know that any part of the application is accessed through index.php, if this script is tried to be accessed without going through index.php, it should exit.
View
In the view folder, we keep the view files which are .php files. We can create subfolders in the view folder if needed.
Models
class Xyz extends CI_Model
{
public function test()
{
return “model test”;
}
}
Calling this model within a controller:
class Welcome extends CI_Controller
{
public function index()
{
$this->load->model('xyz');
$data=$this->xyz->test();
print $data;
$this->load->view('welcome_message');
}
}
We can give the model xyz another name here , say, pqr. Example follows:
class Welcome extends CI_Controller
{
public function index()
{
$this->load->model('xyz',’pqr’);
$data=$this->pqr>test();
print $data;
$this->load->view('welcome_message');
}
}
Connecting To Database : In the following file, we configure the database connection.
application/config/database.php
$active_group = 'default';
$query_builder = TRUE;
$db['default'] = array(
'dsn' => '',
'hostname' => 'localhost',
'username' => '',
'password' => '',
'database' => '',
'dbdriver' => 'mysqli',
'dbprefix' => '',
'pconnect' => FALSE,
'db_debug' => (ENVIRONMENT !== 'production'),
'cache_on' => FALSE,
'cachedir' => '',
'char_set' => 'utf8',
'dbcollat' => 'utf8_general_ci',
'swap_pre' => '',
'encrypt' => FALSE,
'compress' => FALSE,
'stricton' => FALSE,
'failover' => array(),
'save_queries' => TRUE
);
We need to load the database in the model:
class Xyz extends CI_Model
{
public function test()
{
$this->load-database();
$q=$this->db->query(“SELECT * FROM login”);
$result=$q->result();
return $result;
}
}
Calling this model within a controller and passing data to view:
class Welcome extends CI_Controller
{
public function index()
{
$this->load->model('xyz');
$data=$this->xyz->test();
$this->load->view('welcome_message',$data);
}
}
Libraries: CodeIgniter has many libraries of classes useful in many programming situations.
class Welcome extends CI_Controller
{
public function index()
{
$this->load->library(form_validation);
$this->form_validation->fd();
}
}
class Welcome extends CI_Controller
{
public function index()
{
$this->load->library( array(‘form_validation’,’email’) );
//calling an array of libraries.
$this->form_validation;
$this->email;
}
}
Helpers: These are the collection of functions useful in many programming situations.
class Welcome extends CI_Controller
{
public function index()
{
$this->load->helper(‘ ‘);
}
}
Note: If some helper function is needed in a view, that helper should be loaded in the concerned controller first.
Autoloading:
application/config/autoload.php
In this file, there are given several arrays. We need to set the parameters only to get them loaded automatically. In that case, we would not need to write code like: $this->load;
$autoload['libraries'] = array();
$autoload['drivers'] = array();
$autoload['helper'] = array();
$autoload['config'] = array();
$autoload['language'] = array();
$autoload['model'] = array();
Custom Helpers
The built-in helpers of CodeIgniter are kept within the system folder. But within application/helpers, we can create a PHP file as one of our custom helpers. The name pattern is : abc_helper.php.
Now while calling this helper file we use:
$this->load->helper(‘abc’);
Extending Helpers: We can override some built-in helper function or even add something to it from our end.
These files are kept in application/helpers. We should name such a file starting with “MY”, for e.g. MY_abc_helper.php
Let us take the example of array helper of CodeIgniter. $this->load->helper('array');
Now in this helper, there is no function as test(); Let us create a custom helper as
MY_array_helper.php
In this custom helper file, let us define this function- test(). Now this function-test() would run from the array helper of CodeIgniter. So it is like extending a class, though actually, a helper is not a class.
class Welcome extends CI_Controller
{
public function index()
{
$this->load->helper(‘ array‘);
test();
}
}
Similarly, we can override a function in a helper file of CodeIgniter. To do this we need to redefine a helper function of CodeIgniter in our custom helper file.
Basically, it is a very vast topic. But we can summarize by saying that CodeIgniter is a very successful MVC framework that is rich in resources and as light as we can imagine.
